At Westbrook Family Dental in Toowoomba, we frequently see patients who are dealing with various dental issues, and one of the most common complaints we hear is gum pain. While it may seem like a minor irritation, gum pain can actually be a symptom of more serious dental health issues that require professional attention. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore what causes gum pain, the early warning signs to watch for, and how to prevent and treat this discomfort. Understanding these signs early can help you protect your gum health and prevent more severe complications in the future.
1. What Causes Gum Pain?
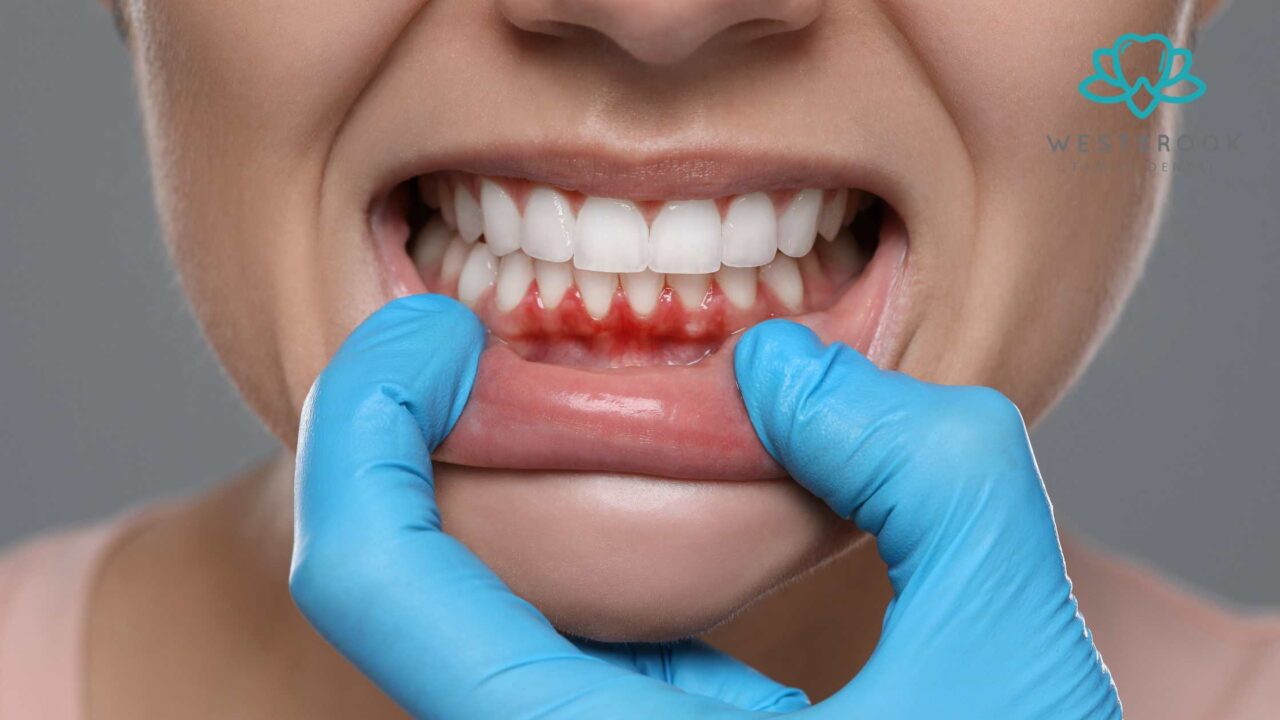
There are several causes of gum pain, ranging from temporary irritation to serious underlying conditions that require immediate dental care. Here’s a closer look at some of the most common reasons you might experience gum pain:
a) Gingivitis and Periodontitis
The most common cause of gum pain is gum disease, which typically starts as gingivitis. Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums due to the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth. The bacteria in plaque produce toxins that irritate the gums, leading to swelling, redness, and gum pain.
- If gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease that can cause significant damage to the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. Periodontitis often leads to deep pockets between the gums and teeth, bone loss, and eventual tooth loss. At this stage, gum pain is often accompanied by bleeding, sensitivity, and loose teeth.
Tip: Regular dental check-ups can help detect and treat gingivitis before it becomes periodontitis. Visit Westbrook Family Dental for preventive care.
b) Tooth Infections and Abscesses
When a tooth becomes infected, particularly at the root, the infection can spread to the surrounding gums, causing gum pain. This type of pain is usually more localized, affecting the area around the infected tooth. An abscess, which is a pocket of pus caused by a bacterial infection, can form in the gums or around the tooth and cause severe gum pain, swelling, and sometimes fever.
- Abscesses should be treated immediately, as the infection can spread to other areas of the mouth or even enter the bloodstream, leading to more serious health issues.
c) Gum Injury or Trauma
Sometimes gum pain is the result of an injury. This could be due to brushing too aggressively, using a toothbrush with hard bristles, or eating hard foods that accidentally cut or damage the gum tissue. While this type of gum pain may be temporary, it’s important to be gentle with your gums and switch to a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent further damage.
d) Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormone levels, especially during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can make your gums more sensitive and prone to swelling, tenderness, and gum pain. This is often referred to as pregnancy gingivitis and affects many women during the course of their pregnancy due to increased blood flow to the gums.
Tip: If you’re pregnant or experiencing hormonal changes, consider scheduling more frequent dental check-ups to stay on top of your gum health.
2. Early Warning Signs of Gum Pain You Shouldn’t Ignore
While gum pain itself is a sign that something isn’t right, there are often other accompanying symptoms that can help identify the severity of the issue. Recognizing these signs early can prevent more serious complications.
a) Red, Swollen Gums
Healthy gums should be a firm, pale pink color. When your gums become red or swollen, it’s a sign of inflammation, often caused by gingivitis. Swollen gums are tender to the touch and may feel puffy or enlarged. Ignoring swollen gums can lead to more severe gum disease, which can cause long-term damage to your oral health.
b) Bleeding Gums
One of the earliest signs of gum disease is bleeding gums. If your gums bleed when you brush, floss, or eat hard foods, it’s a sign that your gums are inflamed. Although occasional bleeding might not seem like a big deal, persistent bleeding is a major indicator of gum disease. Ignoring this symptom could allow gum disease to progress to a more severe stage.
- Tip: To prevent bleeding gums, brush and floss regularly, but be gentle. Avoid aggressive brushing, which can irritate your gums further.
c) Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
Bad breath, or halitosis, is often a sign that bacteria are trapped under the gumline. If your bad breath persists even after brushing and flossing, it could be a sign of gum disease. The bacteria in plaque produce foul-smelling gases, which can be trapped in the gums, leading to persistent bad breath. Halitosis, combined with gum pain, could be an early warning sign of gingivitis or periodontitis.
d) Gum Recession
When the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, it’s known as gum recession. Receding gums expose more of the tooth and sometimes even the root, making the teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods. Gum recession is often a sign of advancing gum disease, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss. Gum recession also makes your teeth appear longer, which can affect the appearance of your smile.
e) Sensitive Teeth
Tooth sensitivity often accompanies gum pain, especially if gum recession has occurred. When the protective enamel is worn down, or the gums recede, the dentin (a more sensitive layer of the tooth) is exposed, causing discomfort when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet foods. If you’re experiencing tooth sensitivity alongside gum pain, it’s important to visit your dentist to determine the underlying cause.
f) Loose Teeth
As gum disease progresses, the supporting tissues and bone that hold your teeth in place can become damaged, causing the teeth to become loose or shift in your mouth. This is a serious sign that gum disease has advanced to periodontitis. Without treatment, loose teeth can eventually fall out, and you may require restorative dental work such as implants or dentures.
- Tip: If your teeth feel loose, it’s crucial to seek dental care immediately. Gum disease can often be managed with prompt treatment, but delaying care can lead to tooth loss.
3. The Link Between Gum Pain and Overall Health

Did you know that your oral health is closely linked to your overall health? Gum disease, which often begins with gum pain, has been associated with several serious health conditions. Here are a few examples:
- Heart Disease: Research has shown that the bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and contribute to the formation of arterial plaque, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes are more susceptible to gum disease due to impaired blood sugar regulation. In turn, gum disease can make it harder to control blood sugar levels, creating a harmful cycle.
- Respiratory Infections: Bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, potentially leading to respiratory infections such as pneumonia.
Ignoring gum pain and the early signs of gum disease not only puts your oral health at risk but could also negatively impact your overall health.
4. How to Prevent Gum Pain
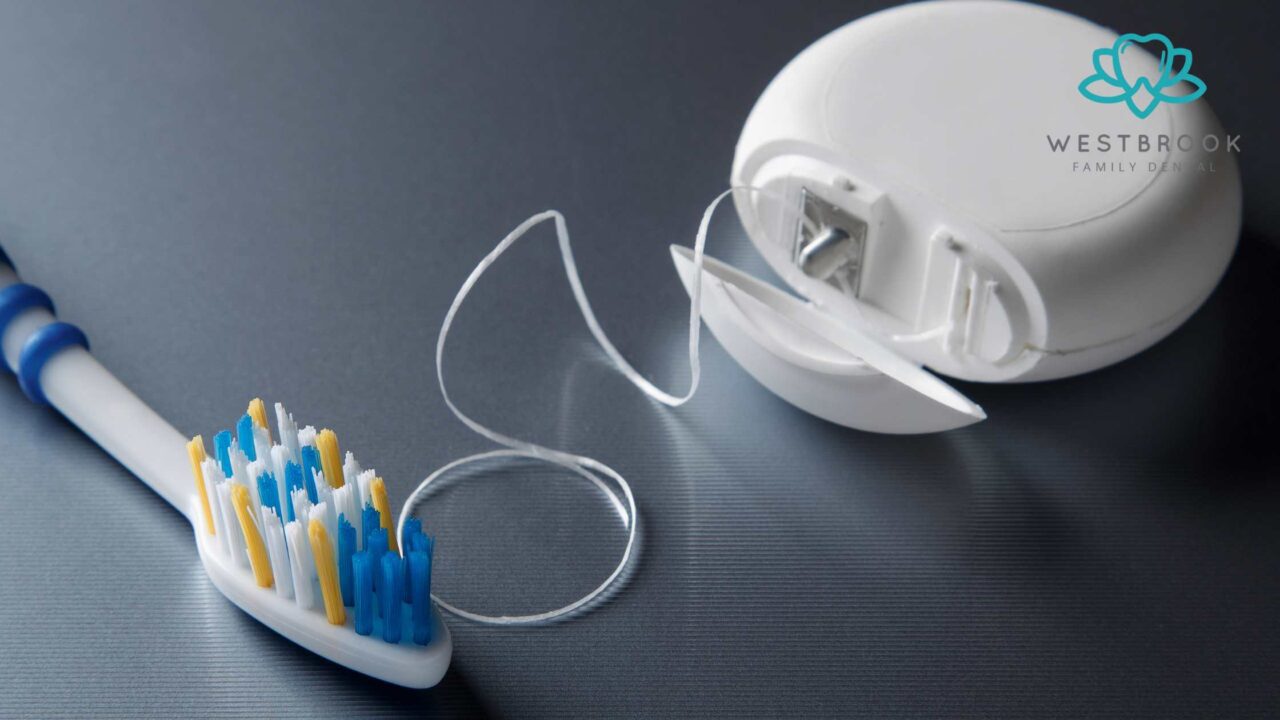

Preventing gum pain starts with maintaining good oral hygiene and making healthy lifestyle choices. Here are the key steps you can take to keep your gums healthy:
- Brush Twice Daily: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush along the gumline, but be gentle to avoid irritating the gums.
- Floss Daily: Flossing removes plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline, where your toothbrush can’t reach. Skipping flossing can allow plaque to build up, leading to gum pain and gum disease.
- Use Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup. This can help keep your gums healthy and pain-free.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off gum infections. It’s also a major risk factor for gum disease.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, helps support healthy gums. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay and gum irritation.
5. When to See a Dentist for Gum Pain
While practicing good oral hygiene can go a long way in preventing gum pain, there are times when professional dental care is necessary. If you notice any of the following symptoms, it’s time to schedule an appointment with your dentist:
- Gum pain that persists for more than a week
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums
- Gum recession or sensitivity
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Persistent bad breath
At Westbrook Family Dental, we offer a range of treatments to help you manage and prevent gum disease. From professional cleanings to more advanced procedures, we’re here to help you maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile.
Book your appointment with Westbrook Family Dental today.
6. Effective Treatments for Gum Pain
Once you’ve been diagnosed with gum disease, it’s important to begin treatment as soon as possible to prevent further damage. Here are some common treatments for gum pain and gum disease:
a) Professional Cleanings
If your gum pain is caused by plaque buildup and early-stage gum disease, your dentist may recommend a professional cleaning. During the cleaning, your dentist or hygienist will remove plaque and tartar from your teeth and gums, helping to reverse the early stages of gum disease.
b) Scaling and Root Planing
For more advanced cases of gum disease, scaling and root planing (also known as deep cleaning) may be necessary. Scaling removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline, while root planing smooths the roots of the teeth to help the gums reattach to the tooth.
c) Laser Gum Treatment
Laser therapy is a minimally invasive treatment option for gum disease. It uses focused light beams to remove infected tissue and bacteria from the gums, promoting healing and reducing gum pain.
d) Surgical Options
In severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be required to restore your gum health. This could include procedures such as gum grafting (to cover exposed roots), flap surgery (to clean deep pockets), or bone grafting (to regenerate lost bone).
Conclusion: Take Action on Gum Pain Today
At Westbrook Family Dental in Toowoomba, we’re dedicated to helping our patients maintain healthy gums and a pain-free smile. If you’re experiencing gum pain or any other symptoms of gum disease, don’t wait—early intervention is key to preventing more serious dental problems. Whether you need a routine cleaning, treatment for gum disease, or advice on how to improve your oral hygiene, we’re here to help.
Book an appointment with Westbrook Family Dental today and take the first step toward a healthier smile.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Pain
Q: What are the early warning signs of painful gums?
A: Early warning signs of painful gums include swelling, redness, tenderness, and bleeding, especially when brushing or flossing. If you notice these symptoms, it may indicate gum disease or other dental issues.
Q: How can home remedies help in relieving gum pain?
A: Home remedies for quick relief from gum pain include warm saltwater rinses, applying a cold compress, using aloe vera gel, and rinsing with chamomile tea. These methods can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
Q: What are the common causes of sore gums?
A: Common causes of sore gums include gingivitis, gum disease, hormonal changes, canker sores, and irritation from dental appliances. Poor oral hygiene can also lead to swollen gums, which are a common symptom of gum issues.
Q: How does brushing and flossing impact gum health?
A: Regular brushing and flossing are crucial for maintaining gum health. They help remove plaque and food particles, preventing gum disease and reducing the chances of developing painful gums. Neglecting these practices can lead to serious dental problems.
Q: When should I consider over-the-counter pain relievers for gum pain?
A: Over-the-counter pain relievers can be considered when experiencing significant discomfort from gum pain. They can provide temporary relief while you seek dental treatment for underlying issues such as gum disease or infections.
Q: Can hormonal changes lead to gum problems?
A: Yes, hormonal changes, especially during pregnancy, menstruation, or menopause, can cause gums to become more sensitive and prone to swelling and inflammation, which may result in painful gums.
Q: What are some symptoms and causes of gum disease?
A: Symptoms of gum disease include swollen gums, bleeding when brushing, persistent bad breath, and receding gums. Causes include plaque buildup, poor oral hygiene, smoking, and certain health conditions.
Q: How can I treat gum pain caused by canker sores?
A: To treat gum pain caused by canker sores, you can use topical treatments, rinse with saltwater, or apply ice for quick relief from gum pain. Maintaining good oral hygiene and avoiding irritants can also help in the healing process.
Q: What dental treatments are available for gum disease?
A: Dental treatments for gum disease may include professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, and in more severe cases, surgery. Early intervention is essential to prevent further complications and painful gums.
Q: Are there any specific home remedies for swollen gums?
A: Yes, some simple home remedies for swollen gums include rinsing with warm saltwater, using tea bags with chamomile, and applying turmeric paste. These methods can help reduce inflammation and provide pain relief.



