- Introduction of Dental Restoration
A. Brief Explanation of Dental Restoration
Dental restoration refers to a wide array of procedures designed to repair or replace damaged or lost teeth. The goal is to restore not only the appearance of the teeth but also their function and health. Restorative procedures range from minor fillings for cavities to more extensive treatments such as crowns, bridges, inlays, onlays, and dental implants. The type of restoration needed depends on the nature and severity of the dental problem, and the optimal solution can be determined in consultation with a dental professional.
B. Importance of Dental Health
Maintaining dental health is vital for overall well-being. Poor oral health can lead to discomfort, pain, and serious infections. Additionally, conditions such as gum disease (periodontitis) and severe tooth decay can have systemic effects, increasing the risk of conditions such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. Moreover, dental health has a significant impact on self-esteem and quality of life, affecting one’s ability to speak, eat, and express emotions. Therefore, regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are crucial in preventing dental issues and preserving overall health.
C. Introduction of Dental Crowns and Bridges as Common Restoration Techniques
Dental crowns and bridges are two common techniques used in restorative dentistry. A dental crown, often called a “cap,” is used to entirely cover or “cap” a damaged tooth or implant. Besides strengthening a damaged tooth, a crown can be used to improve its appearance, shape, or alignment. Dental crowns can be made from several materials, which can include porcelain, ceramics, composite resin, or metal.
On the other hand, a dental bridge is used to replace one or more missing teeth. Bridges span the space where the teeth are missing and are cemented to the natural teeth or implants surrounding that space. These teeth, called abutments, serve as anchors for the bridge, and a replacement tooth is attached to the crowns that cover the abutments. Like crowns, bridges can be made from a variety of materials, including porcelain, alloys, gold, or a combination.
Both dental crowns and bridges play a crucial role in preserving the functional integrity of the oral cavity, improving dental health, and enhancing the aesthetic appearance of one’s smile.
- Dental Restoration
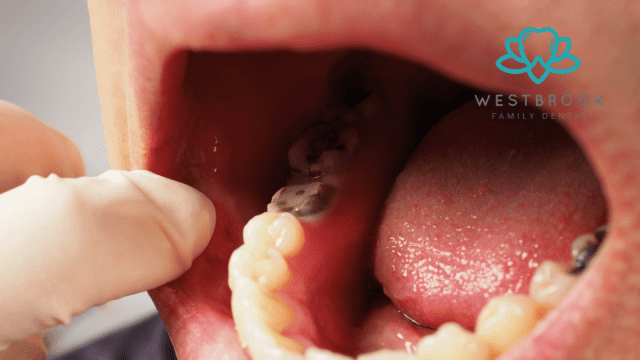
A. The Need for Dental Restoration
Dental restoration becomes necessary when teeth are damaged, decayed, or lost. A host of factors can lead to these issues – from cavities caused by poor oral hygiene and dietary habits to trauma, grinding, and genetic predisposition. Damaged or missing teeth can impact a person’s ability to chew food properly, lead to bite imbalances, cause speech issues, and affect the aesthetics of their smile. Further, leaving such dental issues untreated can lead to more serious complications such as gum disease, bone loss, and systemic infections. Hence, timely dental restoration is key to maintaining oral and overall health.
B. Different Methods of Dental Restoration
Dental restoration encompasses a variety of methods tailored to the specific needs of the patient. For minor tooth decay, fillings made of amalgam, composite, or porcelain are commonly used. Inlays and onlays, which are custom-made fillings, may be used when damage is extensive but doesn’t warrant a crown. If the damage is severe or the tooth is cracked, a crown may be placed to provide strength and protection. Missing teeth can be replaced with bridges, dentures, or dental implants. Root canal treatment is needed when the tooth’s pulp is infected. The specific method of dental restoration chosen depends on the nature and extent of the tooth damage and the overall oral health of the patient.
C. Brief Introduction of Dental Crowns and Bridges in Restoration
Dental crowns and bridges are key tools in the restorative dentist’s toolkit. A dental crown is a tooth-shaped “cap” that is placed over a damaged tooth, restoring its size, shape, strength, and appearance. It is typically used when a large cavity threatens the health of a tooth, after root canal treatment, or to cap a dental implant.
A dental bridge, as the name suggests, is used to “bridge” the gap left by one or more missing teeth. It typically consists of two crowns placed on the teeth on either side of the gap (known as abutment teeth) and a false tooth or teeth in between. These false teeth, known as pontics, can be made from gold, alloys, porcelain, or a combination of these materials. Dental bridges not only restore the appearance of the smile but also distribute the forces in your bite correctly and prevent remaining teeth from shifting out of position.
Exploring the Depths of Dental Health: An In-depth Look at Dental Crowns
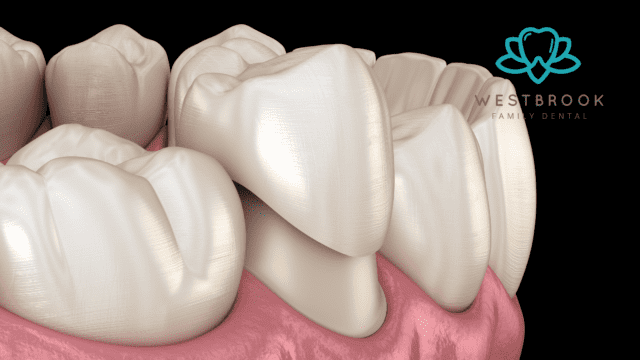
A. Explanation of What a Dental Crown Is
A dental crown, often referred to as a dental cap, is a custom-made restoration that covers the entire visible portion of a damaged tooth or dental implant. It is designed to resemble the natural tooth in shape, size, and color. Dental crowns are typically fabricated from materials such as porcelain, ceramic, metal alloys, or a combination of these, providing strength and durability.
B. When and Why Dental Crowns Are Used
Dental crowns are used in various situations:
– To protect and restore a severely decayed or damaged tooth that cannot be effectively restored with a filling or other dental treatments.
– To strengthen a tooth that has undergone root canal therapy, as it may become more brittle and susceptible to fractures.
– To support and cover a dental implant, replacing a missing tooth.
– To enhance the appearance of a misshapen, discolored, or poorly aligned tooth, improving overall aesthetics and symmetry.
C. The Procedure for Dental Crown Placement
The process of dental crown placement typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Examination: The dentist evaluates the tooth, discusses treatment options, and determines if a dental crown is an appropriate solution.
- Tooth Preparation: The tooth is prepared by removing any decayed or damaged areas, shaping it to accommodate the crown, and ensuring a proper fit.
- Impression: An impression or digital scan of the tooth and surrounding area is taken to create a custom-made crown that matches the natural teeth.
- Temporary Crown: A temporary crown may be placed over the prepared tooth while the permanent crown is being fabricated in a dental laboratory.
- Crown Placement: Once the permanent crown is ready, it is checked for fit, color, and aesthetics. It is then permanently cemented or bonded onto the tooth, ensuring a secure and long-lasting restoration.
D. Different Materials Used for Crowns and Their Advantages
Dental crowns can be made from various materials, each with its own advantages:
– Porcelain or ceramic: These crowns provide excellent aesthetics, closely resembling natural teeth in color and translucency.
– Metal alloys (e.g., gold, nickel-chromium): These crowns offer exceptional strength and durability, particularly for posterior teeth that require greater biting forces.
– Porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM): These crowns combine the strength of metal with the aesthetics of porcelain, providing a balance between durability and natural appearance.
– Zirconia: This material offers excellent strength, durability, and aesthetics, making it a popular choice for dental crowns.
E. Aftercare and Longevity of Dental Crowns
Proper aftercare is crucial for maintaining the longevity of dental crowns:
– Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash.
– Avoid biting on hard objects or using teeth as tools to prevent damage to the crown.
– Schedule regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition of the crown and ensure overall oral health.
– With proper care, dental crowns can last for many years, often ranging from 10 to 15 years or longer, depending on the material used, oral hygiene practices, and individual factors.
Exploring Dental Bridges for Restorative Dentistry
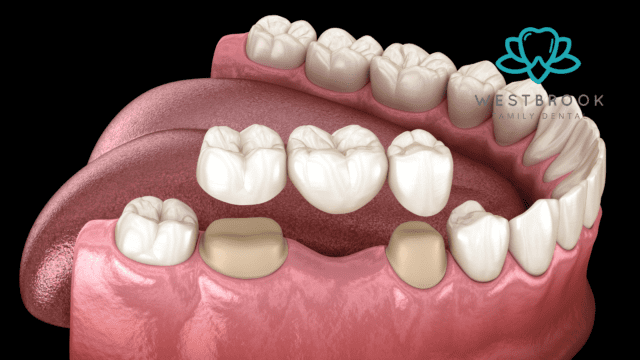
A. Explanation of What a Dental Bridge Is
A dental bridge is a fixed dental restoration that is used to replace one or more missing teeth. It consists of an artificial tooth or teeth, called pontics, which are anchored in place by dental crowns or implants on either side of the gap. The pontics are custom-made to match the appearance and function of natural teeth, restoring the patient’s smile and improving oral health.
B. When and Why Dental Bridges Are Used
Dental bridges are used in the following situations:
– To replace one or more missing teeth, restoring the ability to chew and speak properly.
– To prevent the remaining teeth from shifting out of their positions, which can lead to bite problems and potential dental issues.
– To improve the aesthetics of the smile, enhancing self-confidence and overall facial harmony.
C. The Procedure for Dental Bridge Placement
The placement of a dental bridge typically involves the following steps:
- Consultation and Examination: The dentist assesses the patient’s oral health, discusses treatment options, and determines if a dental bridge is an appropriate solution.
- Tooth Preparation: The abutment teeth (the teeth on either side of the gap) are prepared by removing a portion of the enamel to make space for the dental crowns that will hold the bridge in place.
- Impression: An impression or digital scan is taken to create an accurate model of the prepared teeth and the gap, which serves as the basis for fabricating the bridge and pontics.
- Temporary Bridge: A temporary bridge may be placed while the permanent bridge is being fabricated in a dental laboratory.
- Bridge Placement: Once the permanent bridge is ready, it is checked for fit, aesthetics, and bite alignment. It is then bonded or cemented into place using dental adhesives, ensuring stability and functionality.
D. Different Types of Bridges and Their Advantages
There are several types of dental bridges, including:
– Traditional Bridge: Consists of pontics anchored by dental crowns on the adjacent abutment teeth.
– Cantilever Bridge: Utilizes a single dental crown on one side of the gap for support when adjacent teeth are available on only one side.
– Maryland Bridge: Involves a metal or porcelain framework bonded to the back of adjacent teeth, providing support for the pontics.
– Implant-Supported Bridge: Uses dental implants as the support structure for the bridge, providing excellent stability and function.
The advantages of dental bridges include:
– Restored ability to chew and speak properly.
– Enhanced aesthetics, improving the appearance of the smile.
– Preservation of facial structure and prevention of teeth shifting.
E. Aftercare and Longevity of Dental Bridges
Proper aftercare is essential for maintaining the longevity of dental bridges:
– Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using antimicrobial mouthwash.
– Avoid chewing on excessively hard or sticky foods that can damage the bridge.
– Attend regular dental check-ups to monitor the condition of the bridge and overall oral health.
– With proper care, dental bridges can last for many years, often ranging from 5 to 15 years or longer, depending on the individual’s oral hygiene practices, habits, and overall oral health.
Other Considerations in Dental Restoration
A. Importance of Preventative Care
Preventative care plays a crucial role in dental restoration and overall oral health. It involves maintaining good oral hygiene practices and adopting healthy habits to prevent dental problems before they arise. By prioritizing preventative care, individuals can minimize the need for extensive dental restoration procedures. This includes:
- Brushing and Flossing: Regularly brushing teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily helps remove plaque and bacteria, preventing tooth decay and gum disease.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet that is low in sugary and acidic foods and beverages helps reduce the risk of dental issues such as cavities and enamel erosion.
- Proper Oral Hygiene Techniques: Using the correct brushing and flossing techniques, along with incorporating mouthwash and interdental cleaning tools, promotes optimal oral hygiene.
- Protective Measures: Wearing mouth guards during sports activities and using protective devices such as night guards to prevent teeth grinding can help preserve the integrity of the teeth.
By focusing on preventative care, individuals can maintain better oral health, reduce the need for extensive dental restoration procedures, and enjoy a healthier smile.
B. Role of Regular Dental Visits
Regular dental visits are vital for ensuring optimal dental health and effective dental restoration. Dentists and dental hygienists are trained to detect early signs of dental problems, offer preventive treatments, and provide professional cleanings. Key aspects of regular dental visits include:
- Comprehensive Examinations: Dentists conduct thorough examinations to assess the overall oral health, identify any dental issues or abnormalities, and recommend appropriate treatments.
- Professional Cleanings: Dental hygienists perform deep cleanings to remove plaque, tartar, and surface stains that regular brushing and flossing may miss. This helps prevent gum disease, tooth decay, and other oral health problems.
- X-rays and Diagnostic Tests: Dental X-rays and other diagnostic tests may be conducted to detect hidden dental issues, assess bone health, or plan for specific restoration procedures.
- Treatment Planning: Dentists discuss any identified dental problems and recommend suitable restoration procedures based on individual needs and goals.
- Ongoing Oral Health Maintenance: Dentists provide guidance on proper oral hygiene practices, offer personalized recommendations, and establish regular follow-up schedules to monitor oral health and the success of restoration treatments.
Regular dental visits not only help maintain oral health but also enable early detection and intervention for any emerging dental problems. This proactive approach supports effective dental restoration and promotes long-term oral well-being.
In conclusion, dental crowns and bridges serve as vital tools in restorative dentistry, offering lasting solutions to damaged or missing teeth. By consulting with a trusted dentist, individuals can embark on a journey toward improved oral health, functional restoration, and a confident smile.
FAQ

What are dental crowns?
Dental crowns, also known as dental caps, are custom-made restorations that cover and protect damaged or decayed teeth. They are designed to restore the tooth’s shape, size, strength, and appearance.
How long do dental crowns last?
The lifespan of dental crowns varies depending on various factors, including oral hygiene practices, habits (such as teeth grinding), and the material used for the crown. On average, dental crowns can last between 10 to 15 years or even longer with proper care.
Are dental crowns noticeable or unnatural-looking?
Dental crowns can be made to closely match the color, shape, and appearance of your natural teeth, resulting in a seamless and natural-looking restoration. Advanced techniques and materials enable dentists to create crowns that blend in well with the surrounding teeth.
How are dental crowns placed?
The procedure for dental crown placement typically involves several steps. Firstly, the affected tooth is prepared by removing decay or damage and shaping it to accommodate the crown. Then, impressions or digital scans are taken to create a customized crown. A temporary crown may be placed while the permanent crown is being fabricated. Finally, the permanent crown is bonded or cemented onto the tooth, providing a secure and durable restoration.
What are dental bridges?
Dental bridges are restorations used to replace one or more missing teeth. They consist of artificial teeth (pontics) anchored by dental crowns on adjacent teeth or dental implants.
Can anyone get dental bridges?
Dental bridges are suitable for many individuals with missing teeth, but it depends on factors such as overall oral health, jawbone structure, and the condition of adjacent teeth. A thorough examination and consultation with a dentist can determine if you are a candidate for dental bridges.
How long do dental bridges last?
The lifespan of dental bridges varies, but with proper care and regular dental check-ups, they can last for 10 to 15 years or even longer. Maintaining good oral hygiene and attending regular dental visits are crucial for the longevity of dental bridges.
Are dental bridges removable?
Dental bridges can be either fixed or removable, depending on the specific type of bridge. Traditional bridges are fixed in place and are not removable by the patient. However, there are removable bridges called “removable partial dentures” that can be taken out for cleaning and maintenance.
How do I care for dental crowns and bridges?
Proper oral hygiene is essential for maintaining the health and longevity of dental crowns and bridges. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and rinsing with antimicrobial mouthwash. Additionally, attending routine dental check-ups allows the dentist to monitor the condition of the restorations and provide any necessary maintenance or adjustments.
Can dental crowns and bridges be replaced if needed?
Yes, dental crowns and bridges can be replaced if necessary. Over time, normal wear and tear or changes in oral health may require the replacement of existing crowns or bridges. Consulting with a dentist will help determine if replacement is necessary and what the most suitable options are.



